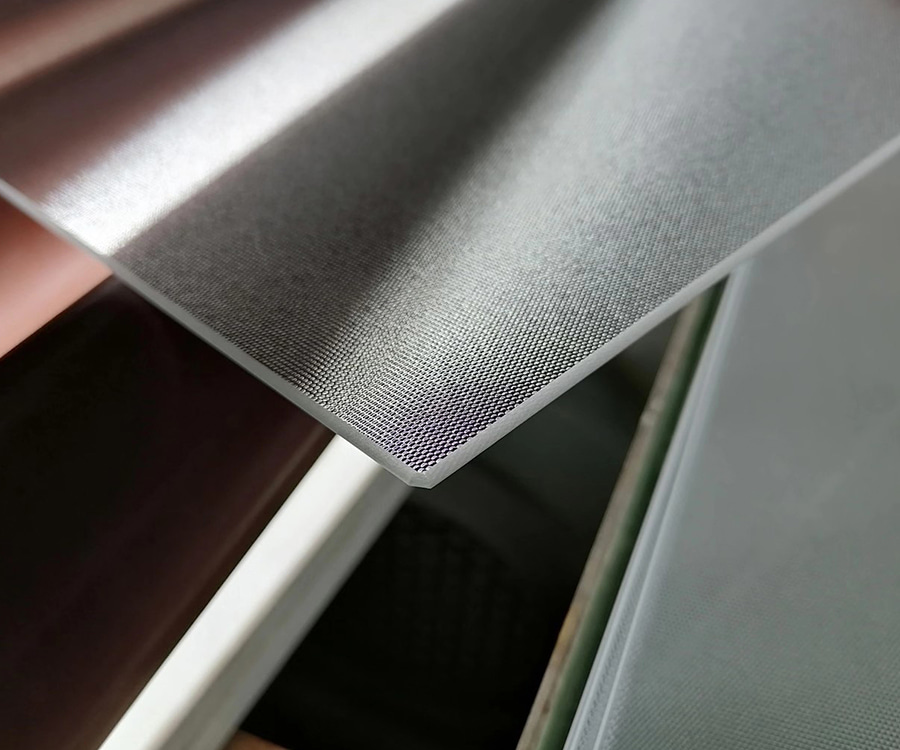
Anti-Reflective Glass, also known as anti-reflective glass, is a glass product with a special coating. Its core function is to significantly reduce excess light reflection from the glass surface, increasing light transmittance to 95% or even higher.
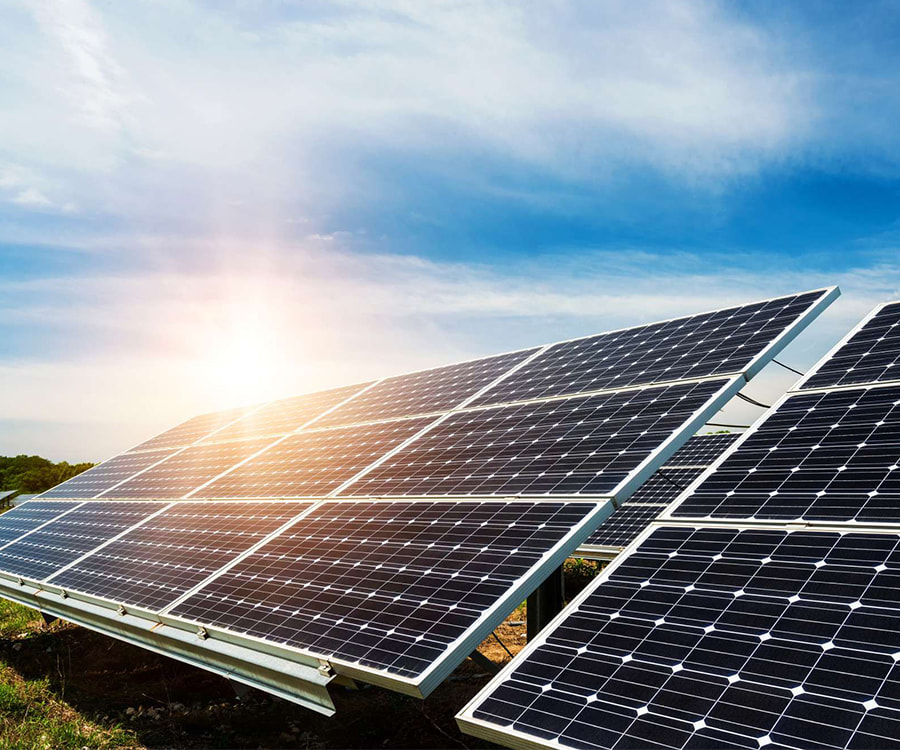
This type of glass is widely used in display devices, building facades, solar panels, museum display cases, and other fields, effectively solving problems such as glare, image overlap, and visual fatigue caused by reflection in traditional glass. However, for any material put into use, a core question always lingers in the minds of users: How long does anti-reflective glass last?
Content
Lifespan of Anti-Reflective Glass: A Comprehensive Answer
The actual lifespan of Anti-Reflective Glass is not a fixed value; it is a variable influenced by a combination of factors. Generally speaking, high-quality anti-reflective glass, under normal use and good maintenance, can last 10 to 20 years, and even longer under certain stable conditions.
However, to obtain a more accurate expectation, we need to understand the following key influencing factors:
1. Core Factor: Coating Technology and Quality
The "anti-reflective" property of anti-reflective glass comes from its multi-layered optical thin film. The quality of this coating is the primary factor determining its lifespan.
- Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): These are the mainstream coating technologies. High-quality coatings have strong adhesion and a dense structure, effectively resisting external abrasion and chemical corrosion.
- Coating Hardness and Adhesion: Excellent AR coatings should have high hardness to resist daily cleaning and light wiping. If the coating adhesion is poor, it is easily detached due to temperature and humidity changes or physical contact, significantly shortening its lifespan.
2. Environmental Factors: Humidity, Temperature, and UV Radiation
The environmental conditions in which the glass is located are significant external stressors affecting the durability of the coating:
- High Humidity and Corrosion: Continuous high humidity, especially air containing acidic or alkaline pollutants, can cause slow chemical corrosion of the coating, leading to fogging or performance degradation.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Extreme temperature changes or rapid thermal cycling can cause a mismatch in the coefficients of thermal expansion between the glass substrate and the coating, inducing stress and ultimately leading to cracking or detachment of the coating.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Exposure: Prolonged exposure to strong UV radiation, especially with improperly selected coating materials, can accelerate the aging and performance degradation of antireflective glass, particularly for outdoor applications such as photovoltaics.
3. Use and Maintenance: Cleaning Habits are Crucial
Improper cleaning and maintenance are common culprits leading to premature failure of antireflective glass:
- Incorrect Cleaning Agents: Using strong acids, alkalis, or cleaners containing abrasive particles can directly damage the optical coating.
- Rough Scrubbing Objects: Wiping with rough cloths or tools with hard objects can scratch the coating, causing irreversible physical damage.
Maintenance Recommendations: It is recommended to use purified water or a dedicated neutral glass cleaner, along with a soft, lint-free microfiber cloth for gentle wiping.
Anti-Reflective Glass is a high-tech product, and its high price reflects its long-term stable performance and lifespan. If you choose antireflective glass that meets international standards and employs advanced magnetron sputtering or PVD technology, and combine this with proper maintenance habits, you can expect it to perform for decades in your applications.