In modern electronics, glass is no longer just a fragile container; it has evolved into a core material supporting semiconductors, display technologies, and communications. From smartphone touchscreens to high-performance sensors, the physical and chemical properties of glass directly determine the durability and functional boundaries of devices.
Content
1. Core Classifications of Electronic-Grade Glass
The electronics field has extremely stringent requirements for materials. Ordinary soda-lime glass, due to its high thermal expansion coefficient and high impurity content, is ill-suited for high-precision tasks. Currently, mainstream applications include:
Aluminosilicate glass: Known for its extremely high hardness and scratch resistance, it is the preferred choice for mobile phone cover glass (such as Corning Gorilla Glass).
Borosilicate glass: Possesses excellent thermal shock resistance and a low dielectric constant, commonly used in power semiconductor packaging and laboratory electronic equipment.
Quartz glass: With extremely high ultraviolet transmittance and high-temperature resistance, it is an indispensable carrier in semiconductor wafer processing.
2. Core Technology: The Rise of Optoelectronic Glass
In the fields of electronic displays and photovoltaics, the application of Optoelectronic Glass is revolutionary. This type of glass, through special surface treatments or coating processes, endows it with photoelectric conversion or transparent conductivity.
Key characteristics of optoelectronic glass:
High transparency and conductivity: By depositing a layer of transparent conductive oxide (such as ITO) on the glass surface, the glass can conduct electricity while remaining transparent, which is the core of touch screens and LCD panels.
Excellent optical management: This type of glass can precisely control the refraction and reflection of light, improving the color saturation of displays and reducing energy consumption.
Multi-functional integration: Modern Optoelectronic Glass can not only display images but also integrate various electronic components such as fingerprint recognition and light sensors.
3. In-depth analysis of electronic application scenarios
With the development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G technologies, the application scenarios of glass in the field of electronics are constantly expanding:
Semiconductor packaging (Glass Core): Industry giants such as Intel are developing glass substrates to replace traditional organic materials, utilizing the flatness and thermal stability of glass to achieve higher-density chip wiring.
Smart Cockpit: Automotive electronics utilize a large amount of Optoelectronic Glass for HUDs (Head-Up Displays) and large curved in-vehicle central control screens.
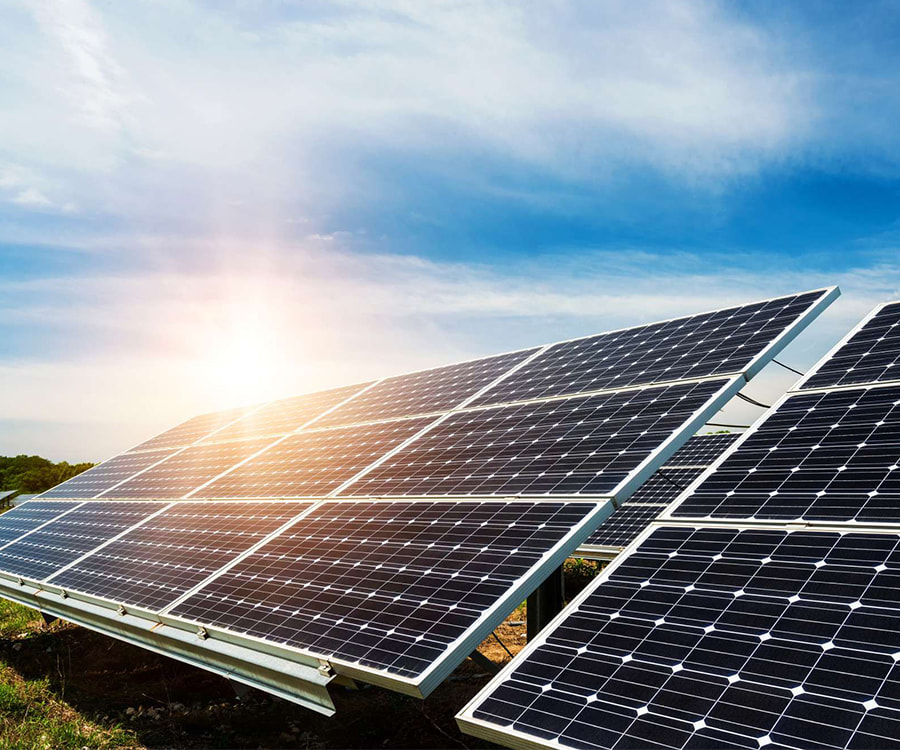
Photovoltaic Electronics: In Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV), special glass serves as both a structural component and a power generation device.
4. Summary and Future Trends
The choice of glass in the electronics field often depends on energy loss, thermal expansion matching, and signal transmission efficiency. Optoelectronic glass, with its unique advantages in photoelectric signal conversion, has become a core driving force in flexible displays, transparent displays, and high-efficiency energy harvesting. With advancements in technology, ultra-thin, flexible glass materials with high conductivity will fundamentally change the way we interact with electronic devices.